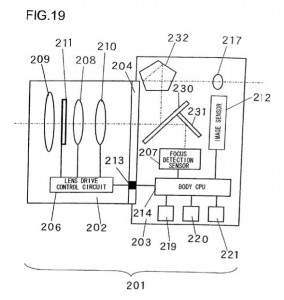
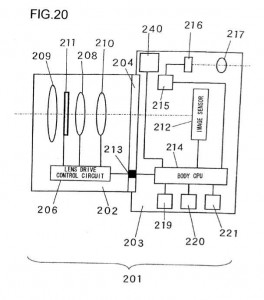
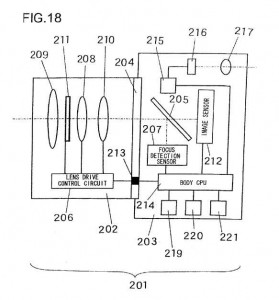
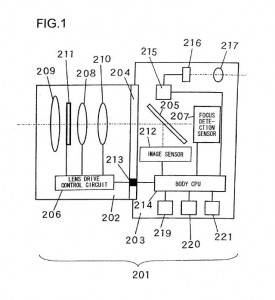
As some readers already noted, this previously covered patent application could be the base of the new continuous AF in video mode/live view feature which will first be implemented in the new Nikon D3100 DSLR camera. As you can see from the drawings, Nikon produced various camera configuration as a possible implementations of this patent, which could indicate that this solution will spread across all future Nikon cameras, including the EVIL system.
Nikon patent application 20100150539 is for a focus adjustment solution (see wikipedia’s explanation of the two different passive focus solutions: phase detection and contrast measurement). Different implementations are shown in this patent application: the first drawing is a camera with a half mirror, the second is mirrorless (EVIL) camera, the third implementations is without a prism (Pellix camera?) and in the last drawing the sensor is located under the mirror (instead of behind the mirror):
Quotes from the patent application after the break:
“Field of the invention: The present invention relates to a device that adjusts the focus of an imaging optical system, an imaging device equipped with the focus adjustment device and a focus adjustment method.
Abstract: A focus adjustment device includes an image sensor that includes imaging pixels for capturing an image formed via an imaging optical system and focus detection pixels for detecting a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a first pupil division-type image shift detection method, a focus detector that detects a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a second pupil division-type image shift detection method different from the first pupil division-type image shift detection method, and a focus adjustment controller that executes focus adjustment for the imaging optical system based upon the focus adjustment states detected by the image sensor and the focus detector.
Description of the related art: There is a digital camera known in the related art (see Japanese Laid Open Patent Publication No. 2001-281530) that includes a focus detection sensor adopting a phase difference detection method and an image sensor. This digital camera first drives the imaging optical system to a point near the focus match position based upon the results of detection executed by the focus detection sensor, then detects the focus match position through a contrast detection method by using the output from the image sensor and executes fine adjustment to the focus match position. However, the contrast detection method and the phase difference detection method adopted in the camera in the related art described above are not perfectly compatible with each other since their focus detection principles are different and, for this reason, the correspondence of the focus detection results obtained through the two methods tends to be poor. For instance, there may be a photographic subject for which the focus can be detected successfully through the phase difference detection method but the focus detection cannot be executed successfully through the contrast detection method. In addition, while the focus may be detected with a high level of accuracy through the phase difference detection method for a given photographic subject, the accuracy of the focus detection for the same photographic subject executed through the contrast detection method may be poor. Under such circumstances, the imaging optical system may hunt for, and fail to reach the focus match point, the imaging optical system may be driven to an unexpected position or the imaging optical system may not move at all when the camera attempts to fine-adjust the position of the imaging optical system through the contrast detection method after driving the lens to a point near the focus match position through the phase difference detection method.”